Acid Base and Salt Notes : Definition Properties and uses. Here we discussed about Most important topic of Class 11 and 12 chemistry
Table of Contents
अम्ल ,क्षारक तथा लवण ( Acid, Base and Salt Notes)
अम्ल (Acid) : Acid Base and Salt Notes
प्रारम्भिक अवधारणाओं के अनुसार , वे पदार्थ जो खट्टे होते हैं तथा नील लिटमस पत्र को लाल कर देते हैं , अम्ल कहलाते हैं |
आर्हेनियस के अनुसार , अम्ल वह पदार्थ है , जो जल में घोलकर हाइड्रोजन आयन (H+) देता है|
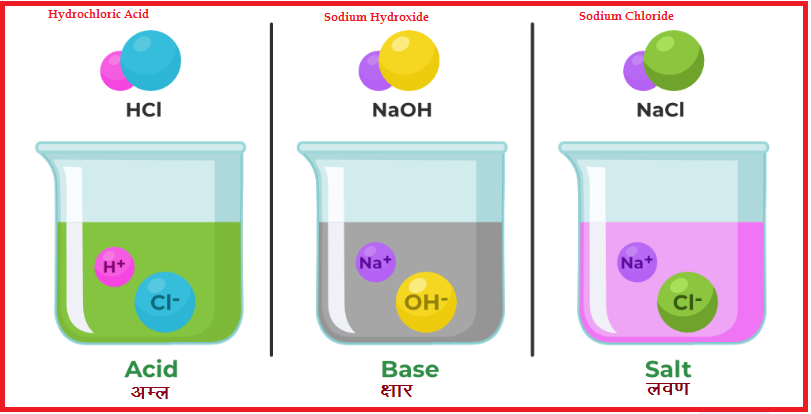
उदाहरण – HCl ,H2SO4 ,HNO3 , CH3COOH आदि
HCl + जल H+(aq) + Cl- (aq)
ब्रान्स्तेड – लारी के अनुसार , अम्ल वह अणु अथवा आयन है जो प्रोटान देने की क्षमता रखता है |
अम्ल H+ + संयुग्मी क्षार प्रोटान
उदाहरण- NH4 + HN 3 + H + HCO – 3 CO 2- 3 + H +
अम्ल दो प्रकार के होते हैं
- ऑक्सी अम्ल जिन अम्लों में हाइड्रोजन एवं ऑक्सीजन दोनों उपस्थित होते हैं | जैसे –
H 2 SO 4 ,HNO 3 - हाइड्रा अम्ल वे अम्ल जिनमें केवल हाइड्रोजन उपस्थित रहता है | जैसे – HCl , HCN
अम्लों के गुणधर्म
अम्ल विधुत के चालक होते हैं |
सक्रिय धातुएँ से क्रिया करके अम्ल हाइड्रोजन मुक्त कारते हैं |
अम्ल , धातु कार्बोनेटों ( तथा धातु बाइकार्बोनेटों ) से अभिक्रिया करके कार्बन
डाइऑंक्साइड गैस मुक्त करते हैं |
अम्ल क्षारकों के साथ क्रिया करके लवण तथा जल बनाते हैं |
अम्लों की प्रकृति संक्षारक होती |
Acid Base and Salt Notes : कुछ अम्ल एवं उनके उपयोग
अम्ल उपयोग
हाइड्रोक्लोरिक अम्ल अम्लराज बनाने में , रंग एवं औषधि निर्माण में |
सल्फ्यूरिक अम्ल विस्फोटक बनाने में , पेट्रोलियम के शोधन में रंग और औषधि में |
नाइट्रिक अम्ल उर्वरक, फोटोग्राफ , अम्लराज में
फार्मिक अम्ल जीवाणुनाशक में , फलों का संरक्षक ,चमड़ा ,रबड़ ,स्कंदन में |
औक्सेलिक अम्ल चमड़े का विरंजन , कपड़े से स्याही का धब्बा हटाने में |
क्षारक (Base) : Acid Base and Salt Notes
प्रारम्भिक अवधारणाओं के अनुसार , वे पदार्थ जो कड़वे होते हैं तथा लाल लिटमस पत्र को नीला कर देते हैं , क्षारक कहलाते हैं|
आर्हिनियस के अनुसार , क्षारक वे पदार्थ हैं जो जल में घुलकर हाइड्राक्सिल आयन ( OH- ) देते हैं |
उदाहरण – Ca(OH)2 , NaOH , NH4OH आदि |
ब्रान्स्तेड – लारी के अनुसार , क्षारक वे अणु या आयन होते हैं जो प्रोटान लेने की क्षमता रखते हैं |
क्षारक + H+ संयुग्मी अम्ल उदाहरण – NH 3 + H + NH 4 + OH – + H + H 2 O
क्षारकों के गुणधर्म
क्षारक ,विधुत के चालक होते हैं |
क्षारक , केवल कुछ धातुओं के साथ क्रिया करके हाइड्रोजन मुक्त करते हैं |
ये , अम्लों से क्रिया करके लवण तथा जल बनाते हैं |
जल में विलेय क्षारकों को क्षार कहते हैं | अतः सभी क्षार ,क्षारक होते हैं जबकि सभी
क्षारक , क्षार नहीं होते |
कुछ क्षारक एवं उनके उपयोग
क्षारक उपयोग
कैल्सियम
हाइड्राक्साइड
विरंजक चूर्ण (ब्लीचिंग पाउडर) के निर्माण में , मिट्टी की अम्लीयता दूर करने में , चमड़े के ऊपर से बाल साफ करने में |
कास्टिक सोडा पेट्रोलियम के शुध्दिकरण में , साबुन बनाने में , कागज बनाने में |
पोटैशियम हाइड्राक्साइड
मुलायम साबुन के निर्माण में तथा कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड ,सल्फर डाइऑक्साइड गैसों के अवशोषण में |
कैल्सियम ऑक्साइड कास्टिक सोडा बनाने में , विरंजक चूर्ण (ब्लीचिंग पाउडर) बनाने में |
मैग्नीशियम हाइड्राक्साइड
अम्ल की विषाक्तीकरण में एंटीडाट के रूप में , चीनी उधोग में पेट की
अम्लीयता दूर करने में |
मैग्नीशियम ऑक्साइड
रबड़ पूरक के रूप में
सूचक (Indicators) : Acid Base and Salt Notes
वे पदार्थ जिनका रंग अम्ल अथवा क्षारक को मिलाने पर परिवर्तित हो जाता है , सूचक कहलाते हैं | अतः इनका प्रयोग किसी पदार्थ की प्रकृति ( अम्लीय /क्षारीय ) जानने के लिए किया जाता है | उदाहरण के लिए फिनालफ्थैलीन , अम्ल के विलयन में रंगहीन होता है जबकि क्षारीय विलयन में इसका रंग लाल होता है | इसी प्रकार , मेथिल ऑरेंज का रंग अम्लीय विलयन में
लाल तथा क्षारीय विलयन में पीला होता है |
कुछ सूचकों एवं अम्लीय तथा क्षारीय विलयनों में उनकें रंगों को आगे सारणीबद्ध किया गया है |
महत्त्वपूर्ण सूचक एवं उनके रंग
| सूचक | सूचक का रंग परिवर्तन | सूचक | सूचक का रंग परिवर्तन |
| अम्लीय विलयन में | क्षारीय विलयन में | ||
| मेथिल ऑरेंज | लाल | मेथिल ऑरेंज | पीला |
| मेथिल रेड | लाल | मेथिल रेड | पीला |
| लिटमस | लाल | लिटमस | नीला |
| फीनाल रेड | पीला | फीनाल रेड | लाल |
| फिनालफ्थैलीन | रंगहीन | फिनालफ्थैलीन | गुलाबी |
PH पैमाना : Acid Base and Salt Notes
किसी पदार्थ के तनु जलीय विलयन की अम्लता या क्षारकता को मापने के लिए सारेंसन ने एक पैमाना विकसित किया जिस पर 1 से 14 तक संख्याएँ अंकित होती हैं | ये संख्याएँ तनु जलीय विलयनों की अम्लता या क्षारकता को Ph के रूप में व्यक्त करती हैं |
1. PH मान 7 होने पर विलयन उदासीन हो जाता है | 7 से कम PH मान अम्लीय विलयन को दर्शाता है जबकि 7 से अधिक PH मान क्षारकीय विलयन को दर्शाता है |
2. PH मान को हाइड्रोजन आयनों की सान्द्रता के रूप में भी व्यक्त किया जा सकता है |
PH = – Log[H+]
अथवा [H+] = 110 -PH PH + POH = 14 तथा [H+][OH-] = 110-14
दैनिक जीवन में प्रयुक्त कुछ पदार्थों के PH मान नीचे दिए गए हैं| Acid Base and Salt Notes
पदार्थ PH मान
आँत्र रस 1.4
नींबू 2.4
सिरका 3.0
टमाटर 4.2
वायु में उपस्थित जल 5.5
दूध 6.4
शुध्द जल ` 7
मानव रक्त या आँसू 7.4
खाने का सोडा 8.4
अंडे 7.8
घरों में प्रयुक्त अमोनिया 11.5
चूना 13
लवण (Salts)
आयनित होकर H+ व OH- बनाते हैं तथा अम्ल एवं क्षारक के बीच उदासीनीकरण क्रिया के
फलस्वरूप बनते हैं , लवण कहलाते हैं |
उदाहरण – NaCl , CH3COONA , K2SO4 आदि
लवणों का वर्गीकरण : Acid Base and Salt Notes
लवणों का वर्गीकरण निम्नलिखित प्रकार से किया जाता है
समान्य लवण – वे लवण , जो अम्ल और क्षार के पूर्ण उदासीनीकरण के फलस्वरूप बनते हैं ,
समान्य लवण कहलाते हैं |
उदाहरण – NaCl , NH4Cl , Na2SO4 आदि |
अम्लीय लवण – वे लवण , जो किसी क्षार के द्वारा किसी अम्ल के अपूर्ण उदासीनीकरण के
फलस्वरूप बनते हैं , अम्लीय लवण कहलाते हैं | :
उदाहरण – NaHSO4 ,NaH2PO4 , KHCO3 आदि |
मिश्रित लवण – वे लवण ,जो अम्ल के दो क्षारों द्वारा अथवा एक क्षार के दो अम्लों द्वारा
उदासीनीकरण के फलस्वरूप बनते हैं मिश्रित लवण कहलाते हैं |
उदाहरण – Ca(Ocl)Cl विरंजक चूर्ण |
द्विक लवण – वे लवण , जो समान्य लवणों के विलयन के वाष्पन के फलस्वरूप बनते हैं , द्विक
लवण कहलाते हैं |
उदाहरण – मोर लवण ( FeSO4.(NH4)2SO4.6H2O )7 फिटकरी आदि |
संकर लवण – वे लवण जो दो यौगिकों की अभिक्रिया के फलस्वरूप बनते हैं तथा बनने वाले
लवण के गुण , प्रयुक्त यौगिकों के गुणधर्मों से भिन्न होते हैं , संकर लवण कहलाते हैं | इन लवणों
में इनके अवयवी आयन अपनी पहचान खो देते हैं |
उदाहरण – पोटैशियम फेरो सायनाइड K 4 [Fe(CN) 6 ] (यह लवण Fe 2+ तथा CN – आयनों का
परीक्षण नहीं देता ) |
To buy Motivational e-Books visit https://yorhelp.shop
Acids, Bases and Salt Notes in English :
Let’s learn all about acids, bases and salts in English language through this section.
Acid :
According to the initial concepts, substances which are sour and turn blue litmus paper into red
are called acids.
According to Arrhenius, acid is that substance which, when dissolved in water, gives hydrogen ion (H+).
,
Example – HCl, H2SO4, HNO3, CH3COOH etc.
HCl + Water H+(aq) + Cl- (aq)
According to Brønsted-Lory, an acid is a molecule or ion which has the ability to give a proton.
Keeps
Acid H+ + Conjugate Base
proton
Example- NH4 + HN 3 + H +
HCO – 3 CO 2- 3 + H +
There are two types of acids
- Oxy acids – Acids in which both hydrogen and oxygen are present. As –
H 2 SO 4 ,HNO 3 - Hydra acids are those acids in which only hydrogen is present. Like – HCl, HCN
Properties of Acids : Acid Base and Salt Notes
- Acids are conductors of electricity.
- Acids liberate hydrogen by reacting with active metals.
- Carbon reacts with acids, metal carbonates (and metal bicarbonates)
- Release dioxide gas.
- Acids react with bases to form salts and water.
- Acids are corrosive in nature.
Some Acids and their uses
Use of Acids :
Hydrochloric acid is used in making Amlaraj, in manufacturing of colors and medicines.
Sulfuric acid is used in making explosives, in refining petroleum, in dyes and medicines.
Nitric acid fertilizer, photograph, in Amlaraj
Formic acid is used in bactericide, fruit preservative, leather, rubber, coagulation.
Oxalic acid is used in bleaching leather and removing ink stains from clothes.
What is Base? : Acid Base and Salt Notes
According to the initial concepts, substances which are bitter and show red litmus paper are
Turns it blue, is called base.
According to Arrhenius, bases are those substances which dissolve in water and give hydroxyl ions (OH-).
are
Example – Ca(OH)2, NaOH, NH4OH etc.
According to Brønsted-Lory, bases are those molecules or ions which have the ability to accept proton.
are
base + H+ conjugate acid
Example – NH 3 + H + NH 4 +
OH- + H + H 2 O
Properties of bases : Acid Base and Salt Notes
- Bases are conductors of electricity.
- Bases react with only a few metals to liberate hydrogen.
- They react with acids to form salts and water.
- Bases soluble in water are called bases. Hence all bases are bases while all
- Bases are not bases.
Some bases and their uses
- alkali use
- calcium
- hydroxide
In the manufacture of bleaching powder, the acidity of the soil
To remove, to clean hair from the skin.
Caustic soda is used in purification of petroleum, in making soap, in making paper.
potassium
hydroxide
In the manufacturing of soft soap and carbon dioxide, sulfur
In absorption of dioxide gases.
In making calcium oxide caustic soda, in making bleaching powder.
magnesium
hydroxide
As an antidote to acid poisoning, in the sugar industry.
In removing acidity.
magnesium
oxide
as rubber filler
Indicator : Acid Base and Salt Notes
Those substances whose color changes on adding acid or base are called indicators.
are Therefore, they are used to know the nature of a substance (acidic/alkaline).
is. For example, phenolphthalein is colorless in acid solution, whereas in alkaline solution it is colorless.
Its color is red in solution. Similarly, the color of methyl orange in acidic solution is
It is red and yellow in alkaline solution.
Some indicators and their colors in acidic and alkaline solutions are tabulated further.
,
Important indicators and their colors
indicator indicator color change
in acidic solution in alkaline solution
methyl orange red yellow
methyl red red yellow
litmus red blue
phenol red yellow red
Phenolphthalein colorless pink
pH scale
To measure the acidity or basicity of a dilute aqueous solution of a substance, Saranson used a
Developed a scale on which numbers from 1 to 14 are marked. These numbers are dilute aqueous
The acidity or basicity of solutions is expressed as Ph.
When PH value is 7 the solution becomes neutral. Acidic solution with PH value less than 7
Whereas PH value more than 7 indicates alkaline solution.
PH value can also be expressed as the concentration of hydrogen ions.
PH = – Log[H+]
Or [H+] = 110 -PH PH + POH = 14 And [H+][OH-] = 110-14
PH values of some substances used in daily life are given below
substance PH value
intestinal juice 1.4
lemon 2.4
Vinegar 3.0
Tomato 4.2
Water present in air 5.5
milk 6.4
Pure water ` 7
Human blood or tears 7.4
baking soda 8.4
eggs 7.8
Ammonia used in homes 11.5
lime 13
salt
By ionizing, they form H+ and OH- and in the process of neutralization between acid and base.
As a result, they are called salts.
Example – NaCl, CH3COONA, K2SO4 etc.
Classification of salts
Salts are classified as follows
Common salts – Those salts, which are formed as a result of complete neutralization of acid and base,
are called common salts.
Example – NaCl, NH4Cl, Na2SO4 etc.
Acidic salts – Those salts which form due to incomplete neutralization of an acid by a base.
As a result, they are called acidic salts.
Example – NaHSO4, NaH2PO4, KHCO3 etc.
Mixed salts – Those salts which are formed by two bases of an acid or by two acids of one base.
The salts formed as a result of neutralization are called mixed salts.
Example – Ca(Ocl)Cl bleaching powder.
Double salts – Those salts, which are formed as a result of evaporation of solutions of common salts,